Understanding Architectural Mesh Open Area: A Comprehensive Guide
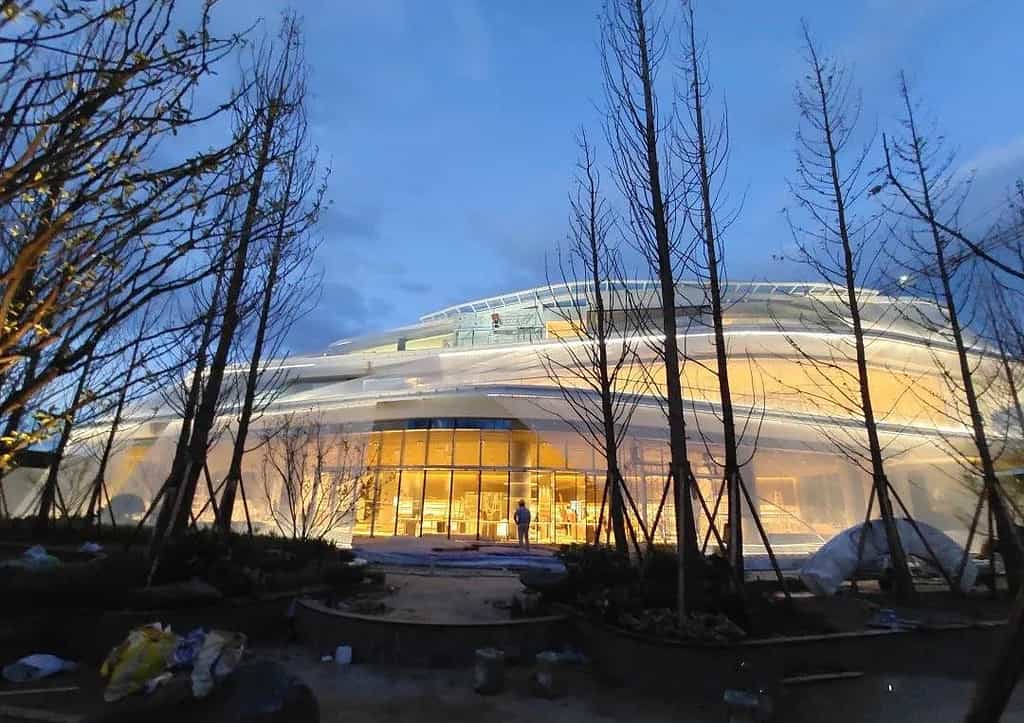

What is architectural mesh open area?
Architectural mesh open area refers to the percentage of open space within a mesh structure.
This open space can vary depending on the type of mesh and its intended use.
For example, a mesh with a higher open area may be used for decorative purposes, while a mesh with a lower open area may be used for security or privacy reasons.
Understanding the open area of a mesh is important in determining its functionality and suitability for a particular application.

How is open area calculated?
Open area is calculated by measuring the total area of the mesh and subtracting the area taken up by the wires or strands that make up the mesh.
This calculation results in a percentage that represents the amount of open space within the mesh.
It’s important to note that open area can vary depending on the orientation of the mesh, as well as the diameter and spacing of the wires or strands.
Architects and designers must carefully consider these factors when selecting a mesh for a specific application.
What are the benefits of high open area?
High open area in architectural mesh offers several benefits. Firstly, it allows for greater airflow and ventilation, which can be important in applications such as building facades or sun shading systems.
Additionally, high open area can provide better visibility and transparency, allowing for natural light to pass through and creating a more open and inviting space.
Finally, high open area can also reduce the weight and cost of the mesh, as less material is required to achieve the desired level of strength and durability.
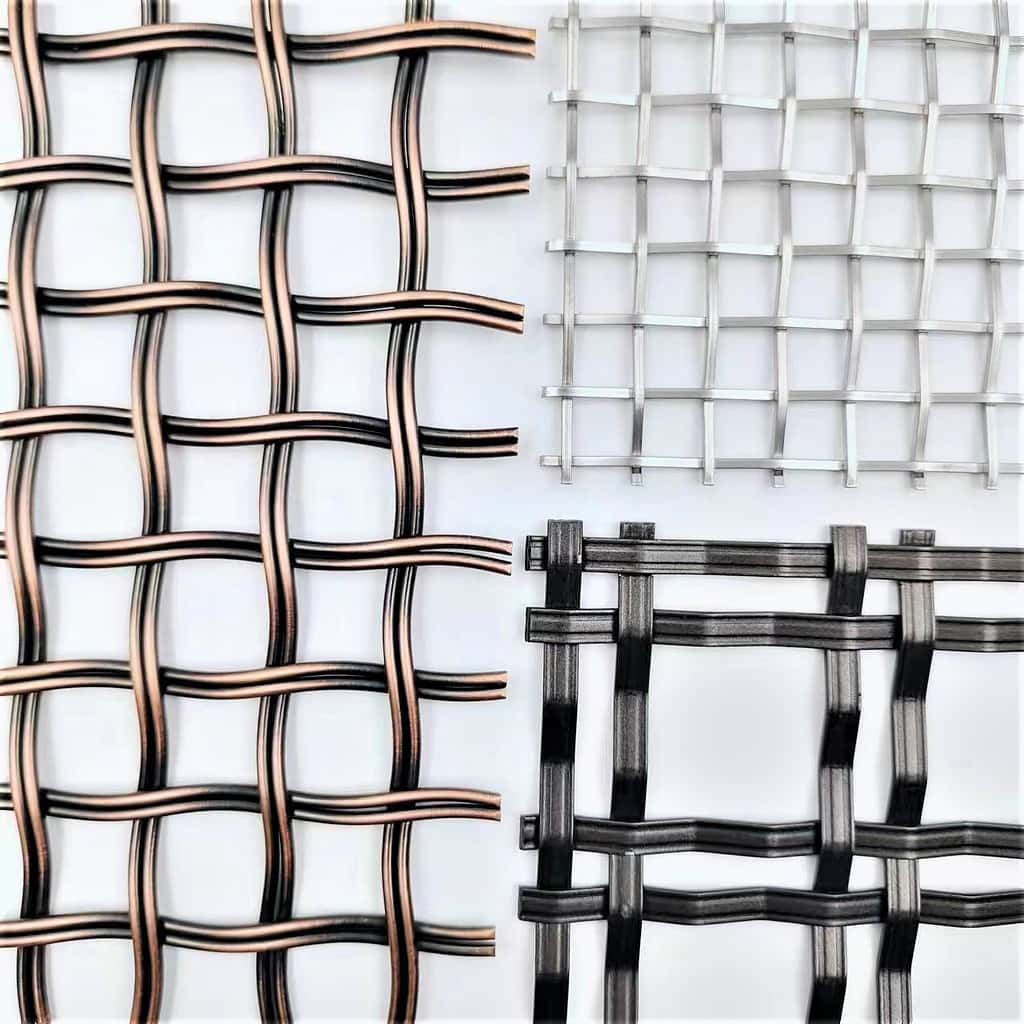
What are the different types of architectural mesh?
There are several different types of architectural mesh, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Some of the most common types include woven wire mesh, welded wire mesh, expanded metal mesh, and perforated metal mesh.
Woven wire mesh is made by weaving individual wires together in a criss-cross pattern, while welded wire mesh is made by welding the wires together at their intersections.
Expanded metal mesh is created by cutting and stretching a sheet of metal, while perforated metal mesh is made by punching holes in a sheet of metal.
Each type of mesh has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which to use will depend on the specific needs of the project.
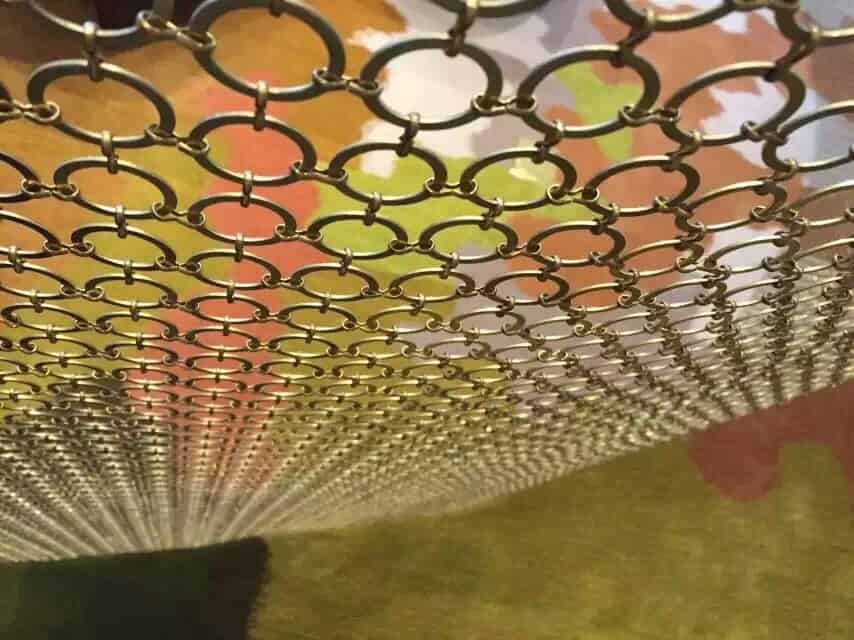

How is architectural mesh used in various applications?
Architectural mesh is a versatile material that can be used in a wide range of applications. It is commonly used in building facades, sunscreens, interior design elements, and even as safety barriers.
In building facades, architectural mesh can be used to create a unique and visually striking appearance, while also providing shade and ventilation.
Sunscreens made from architectural mesh can help to reduce heat gain and glare, while still allowing natural light to enter the building. Interior design elements such as room dividers, wall panels, and ceiling tiles can also be made from architectural mesh, adding a modern and industrial look to any space.
Finally, architectural mesh can be used as safety barriers in areas such as staircases, balconies, and walkways, providing a secure and durable solution.
